ACCT 241 Practice Exam II | American University | American University
- american-university / ACCT 241
- 09 Aug 2019
- Price: $20
- Other / Other
ACCT 241 Practice Exam II | American University | American University
1.
Assume
a company sells a single product. If Q equals the level of output, P is the
selling price per unit, V is the variable expense per unit, and F is the fixed
expense, then the break-even point in sales dollars is:
Multiple Choice
F/(P-V).
F/[Q(P-V)].
F/[Q(P-V)/P].
F/[(P-V)/P].
2.
Sales in North Corporation increased from $60,000
per year to $63,000 per year while net operating income increased from $10,000
to $12,000. Given this data, the company's degree of operating leverage must
have been:
Multiple Choice
4.0
1.5
5.0
21.0
3.
The fixed expenses of the entire company were
$30,970. If the sales mix were to shift toward Product D08Q with total dollar
sales remaining constant, the overall break-even point for the entire company:
Multiple Choice
would
increase.
would decrease.
would
not change.
could
increase or decrease.
4.
Trumbull
Corporation budgeted sales on account of $120,000 for July, $211,000 for
August, and $198,000 for September. Experience indicates that none of the sales
on account will be collected in the month of the sale, 60% will be collected
the month after the sale, 36% in the second month, and 4% will be
uncollectible. The cash receipts from accounts receivable that should be
budgeted for September would be:
Multiple Choice
$169,800
$147,960
$197,880
$194,760
5.
Marst Corporation's
budgeted production in units and budgeted raw materials purchases over the next
three months are given below:
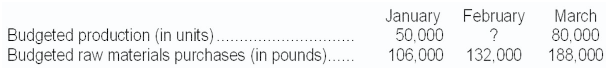
Two pounds of raw materials are required to produce
one unit of product. The company wants raw materials on hand at the end of each
month equal to 30% of the following month's production needs. The company is
expected to have 30,000 pounds of raw materials on hand on January 1. Budgeted
production for February should be:
Multiple Choice
60,000
units
54,000
units
84,000
units
108,000
units
6.
Vandel Inc. bases its selling and administrative
expense budget on budgeted unit sales. The sales budget shows 6,600 units are
planned to be sold in April. The variable selling and administrative expense is
$9.70 per unit. The budgeted fixed selling and administrative expense is
$127,380 per month, which includes depreciation of $8,580 per month. The
remainder of the fixed selling and administrative expense represents current cash
flows. The cash disbursements for selling and administrative expenses on the
April selling and administrative expense budget should be:
Multiple Choice
$191,400
$118,800
$64,020
$182,820
7.
|
The
Wright Company has a standard costing system. The following data are
available for September: |
|
Actual
quantity of direct materials purchased |
70,000
|
pounds |
|
Standard
price of direct materials |
$8
|
per
pound |
|
Material
price variance |
$3,500
|
unfavorable |
|
Material
quantity variance |
$2,500
|
favorable |
|
The actual price per pound of direct materials purchased in September is: (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) |
Multiple Choice
$7.93
$8.00
$8.05
$8.07
8.
|
Blue
Corporation's standards call for 4,125 direct labor-hours to produce 1,650
units of product. During May 1,150 units were produced and the company worked
1,550 direct labor-hours. The standard hours allowed for May production would
be: |
Multiple
Choice
4,125
hours
1,550
hours
2,875
hours
2,975 hours
9.
|
The
following standards for variable manufacturing overhead have been established
for a company that makes only one product: |
|
Standard
hours per unit of output |
7.2 |
hours |
|
Standard
variable overhead rate |
$13.60 |
per
hour |
|
The
following data pertain to operations for the last month: |
|
Actual
hours |
2,750 |
hours |
|
Actual
total variable manufacturing overhead cost |
$38,090 |
|
|
Actual
output |
250 |
units |
|
What
is the variable overhead efficiency variance for the month? |
Multiple Choice
$13,610
U
$12,920
U
$690
F
$24,480 F
10.
|
Given
the following data: |
|
Average
operating assets |
$688,000
|
|
Total
liabilities |
$103,200 |
|
Sales |
$344,000 |
|
Contribution
margin |
$196,080 |
|
Net
operating income |
$61,920 |
|
Return
on investment (ROI) would be: |
Multiple Choice
18.0%
9.0%
57.0%
28.5%
11.
|
Last
year a company had sales of $350,000, a turnover of 2.2, and a return on
investment of 46.2%. The company's net operating income for the year was: |
Multiple Choice
$88,200
$159,091
$161,700
$73,500
12.
Given the following data:
|
Return
on investment |
30%
|
|
Turnover |
2.2
|
|
Margin |
9%
|
|
Sales |
$220,000
|
|
Average
operating assets |
$66,000
|
|
Minimum
required rate of return |
20%
|
|
The
residual income would be: |
Multiple Choice
$6,600
$0
$13,860
$24,200
13.
Lampshire Inc. is considering using stocks of an old
raw material in a special project. The special project would require all 150
kilograms of the raw material that are in stock and that originally cost the
company $2,346 in total. If the company were to buy new supplies of this raw
material on the open market, it would cost $7.90 per kilogram. However, the
company has no other use for this raw material and would sell it at the
discounted price of $7.20 per kilogram if it were not used in the special
project. The sale of the raw material would involve delivery to the purchaser
at a total cost of $74 for all 150 kilograms. What is the relevant cost of the
150 kilograms of the raw material when deciding whether to proceed with the
special project?
Multiple Choice
$1,080
$1,006
$1,165
$1,185
14.
|
The
management of Heider Corporation is considering dropping product H58S. Data
from the company's accounting system appear below: |
|
Sales |
$920,000 |
|
Variable
expenses |
$386,000 |
|
Fixed
manufacturing expenses |
$368,000 |
|
Fixed
selling and administrative expenses |
$248,000 |
|
In
the company's accounting system all fixed expenses of the company are fully
allocated to products. Further investigation has revealed that $229,000 of
the fixed manufacturing expenses and $190,000 of the fixed selling and
administrative expenses are avoidable if product H58S is discontinued. What
would be the effect on the company's overall net operating income if product
H58S were dropped? |
Multiple Choice
Overall
net operating income would decrease by $82,000.
Overall
net operating income would increase by $115,000.
Overall
net operating income would increase by $82,000.
Overall
net operating income would decrease by $115,000
15
|
Consider
the following production and cost data for two products, L and C: |
|
|
Product
L |
Product
C |
|
Contribution
margin per unit |
$32
|
$30
|
|
Machine-hours
needed per unit |
4
hours |
3
hours |
|
The
company can only perform 15,000 machine hours each period, due to limited
skilled labor and there is unlimited demand for each product. What is the
largest possible total contribution margin that can be realized each period? |
Multiple Choice
$135,000
$137,500
$150,000
$165,000
16.
Menlo Company distributes a single product. The
company’s sales and expenses for last month follow:
|
|
Total
|
Per
Unit |
|||
|
Sales |
$ |
616,000 |
|
$ |
40
|
|
Variable
expenses |
|
431,200 |
|
|
28
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contribution
margin |
|
184,800 |
|
$ |
12
|
|
Fixed
expenses |
|
152,400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net
operating income |
$ |
32,400 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Required: |
|
|
1. |
What
is the monthly break-even point in unit sales and in dollar sales? |
|
2. |
Without
resorting to computations, what is the total contribution margin at the
break-even point? |
|
3-a |
How
many units would have to be sold each month to earn a target profit of
$69,600? Use the formula method. |
||
|
|||
|
|||
|
3-b. |
Verify
your answer by preparing a contribution format income statement at the target
sales level. |
|
|
|
4. |
Refer
to the original data. Compute the company's margin of safety in both dollar
and percentage terms. Round your
percentage answer to 2 decimal places (i.e .1234 should be entered as 12.34). |
|
5. |
What
is the company’s CM ratio? If monthly sales increase by $58,000 and there is
no change in fixed expenses, by how much would you expect monthly net operating
income to increase? |
Pearl
Products Limited of Shenzhen, China, manufactures and distributes toys
throughout South East Asia. Three cubic centimeters (cc) of solvent H300 are
required to manufacture each unit of Supermix, one of the company’s products.
The company now is planning raw materials needs for the third quarter, the
quarter in which peak sales of Supermix occur. To keep production and sales
moving smoothly, the company has the following inventory requirements:
- The
finished goods inventory on hand at the end of each month must equal 2,000
units of Supermix plus 25% of the next month’s sales. The finished goods
inventory on June 30 is budgeted to be 14,250 units.
- The
raw materials inventory on hand at the end of each month must equal one-half
of the following month’s production needs for raw materials. The raw
materials inventory on June 30 is budgeted to be 75,375 cc of solvent
H300.
- The
company maintains no work in process inventories.
A
monthly sales budget for Supermix for the third and fourth quarters of the year
follows.
|
|
Budgeted
Unit Sales |
|
July |
49,000 |
|
August |
54,000 |
|
September |
64,000 |
|
October |
44,000 |
|
November |
34,000 |
|
December |
24,000 |
|
|
|
Required:
1.
Prepare a production budget for Supermix for the months July, August, September,
and October.
3. Prepare a direct materials budget showing the quantity of solvent H300 to be purchased for July, August, and September, and for the quarter in total.
18.
|
Dawson
Toys, Ltd., produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently established
a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the
following standards for the Maze toy: |
|
Direct
materials: 8 microns per toy at $0.33 per micron |
|
Direct
labor: 1.2 hours per toy at $7.00 per hour |
|
During
July, the company produced 5,000 Maze toys. Production data for the month on
the toy follow: |
|
Direct materials: 74,000 microns were purchased
at a cost of $0.30 per micron. 24,000 of these microns were still in
inventory at the end of the month. |
|
Direct labor: 6,400 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of
$48,640. |
|
Required: |
|
|
1. |
Compute
the following variances for July: (Indicate
the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable,
"U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero
variance). Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the
nearest whole dollar.) |
|
a. |
The
materials price and quantity variances. |
||
|
||||
|
||||
|
b. |
The labor rate and efficiency variances. 19. Provide the missing data in the following table for
a distributor of martial arts products: (Enter
"Turnover" and "ROI" answers to 1 decimal place.)
20. Delta
Company produces a single product. The cost of producing and selling a single
unit of this product at the company’s normal activity level of 91,200 units per
year is:
The
normal selling price is $22.00 per unit. The company’s capacity is 112,800
units per year. An order has been received from a mail-order house for 1,800
units at a special price of $19.00 per unit. This order would not affect
regular sales or the company’s total fixed costs. Required: 1.
What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) of accepting the special order? 2.
As a separate matter from the special order, assume the company’s inventory
includes 1,000 units of this product that were produced last year and that are
inferior to the current model. The units must be sold through regular channels
at reduced prices. The company does not expect the selling of these inferior
units to have any effect on the sales of its current model. What unit cost is
relevant for establishing a minimum selling price for these units? Required 1 What is the financial advantage (disadvantage) of
accepting the special order? Required 2 As a separate matter from the special order, assume
the company’s inventory includes 1,000 units of this product that were produced
last year and that are inferior to the current model. The units must be sold
through regular channels at reduced prices. The company does not expect the
selling of these inferior units to have any effect on the sales of its current
model. What unit cost is relevant for establishing a minimum selling price for
these units? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||







 USA
USA  India
India
Question Attachments
0 attachments —